Pregnancy & Nursing Benefits
DHA During Pregnancy and DHA While Breastfeeding
Maternal nutrition before, during and after pregnancy plays an important role in fetal and infant development, as well as in maternal well-being. During pregnancy, DHA supports optimal infant brain, eye and nervous system development and is particularly important in the third trimester when significant brain growth occurs. Developing infants cannot efficiently produce their own DHA and must obtain this vital nutrient through the placenta during pregnancy and from breast milk after birth. Maternal DHA supplementation during pregnancy and nursing significantly enhances the level of DHA available to the fetus and infant and may improve certain developmental outcomes, such as:
- Eye-hand coordination
- Motor skills
- Attention span
DHA also provides important maternal benefits. It is suggested DHA supplementation during pregnancy can help lengthen gestation length and support the mental state of the mother.
The Importance of DHA During Pregnancy and Nursing
Breast milk naturally contains DHA. Therefore, it is important that breastfeeding women consume a healthy diet that includes these important nutrients to support both their health and the health of their developing infant.
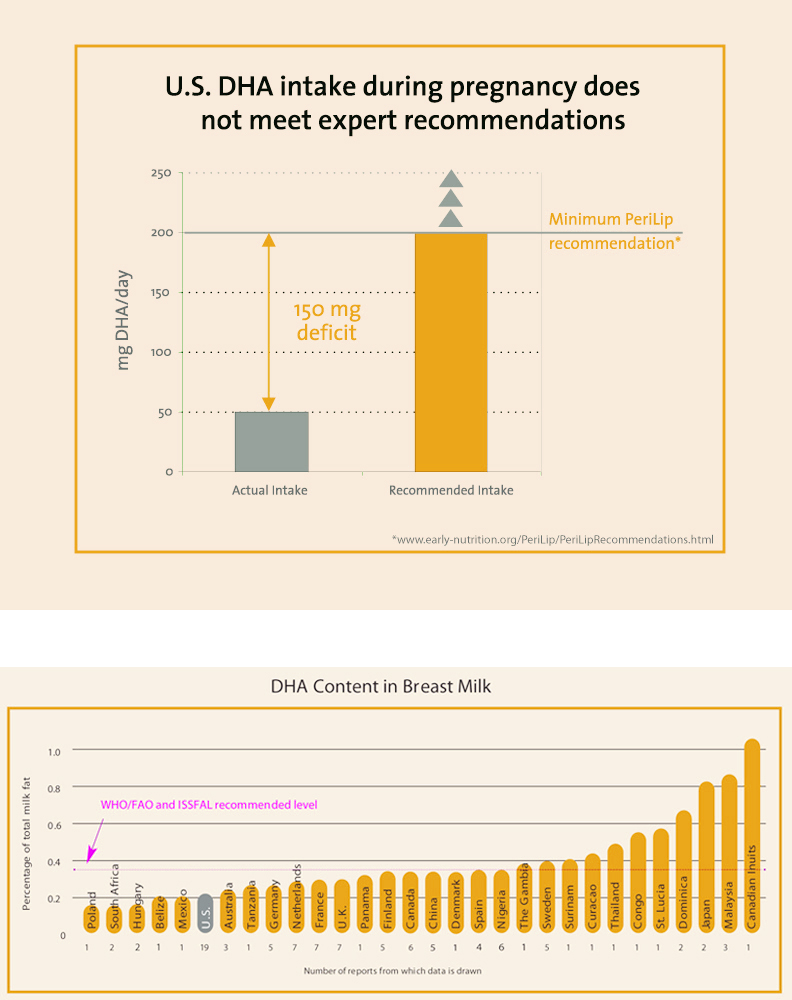
Most women do not get enough DHA in their diets. The primary source of DHA is fatty fish, a dietary choice that is not a staple of the typical Western diet. Fortunately, a growing awareness of the dietary sources of DHA and the recent inclusion of DHA in certain prenatal products and fortified foods are making it easier for women who are breastfeeding to include this important nutrient in their diets every day.
Recognizing the importance of maternal DHA intake, a workshop sponsored by the National Institutes of Health and International Society for the Study of Fatty Acids and Lipids (NIH/ISSFAL) recommended an intake of 300mg/day of DHA for pregnant and nursing women.